Starting a business in India has become more streamlined thanks to government initiatives such as Startup India, MCA’s digital services, and various state-level schemes.
Registering a startup in India is not just about legal compliance—it’s about creating a strong foundation for your entrepreneurial journey, unlocking funding opportunities, and building credibility.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through how to register a startup company in India, the types of business structures available, the necessary documentation, compliance requirements, and practical tips to ensure your startup thrives.
Why Registering a Startup in India is Important
Registering your startup is more than a legal formality—it brings multiple advantages:
- Legal Recognition: Registered businesses are recognized by government authorities and can enter contracts, apply for loans, and avail schemes.
- Funding Opportunities: Investors and venture capitalists prefer startups that are legally registered.
- Brand Credibility: A registered startup gains trust among customers, partners, and suppliers.
- Tax Benefits: Startups can avail exemptions and benefits under the Startup India scheme.
- Intellectual Property Protection: Registration enables you to secure patents, trademarks, and copyrights.
Types of Business Structures in India
Selecting the right business structure is the first step in registering your startup. Each type has its own legal, financial, and tax implications.
1. Proprietorship
A proprietorship is the simplest form of business where an individual owns and manages the business.
- Advantages: Easy to set up, minimal compliance, full control.
- Disadvantages: Unlimited liability, difficult to raise funds, limited credibility.
2. Partnership
A partnership firm involves two or more individuals sharing profits and liabilities.
- Advantages: Simple registration, shared responsibility, flexible structure.
- Disadvantages: Unlimited liability, disputes among partners can affect business.
3. Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)
LLP combines benefits of a partnership and a company. Liability is limited to investment.
- Advantages: Limited liability, separate legal entity, flexible management.
- Disadvantages: More compliance than a partnership, annual filing required.
4. Private Limited Company
Most startups prefer Private Limited Companies (Pvt Ltd) because of credibility and investor-friendly structure.
- Advantages: Limited liability, ability to raise funds, perpetual succession.
- Disadvantages: More compliance, registration cost higher than LLP or partnership.
5. Public Limited Company
A Public Limited Company can offer shares to the public. Suitable for large businesses with high capital requirements.
- Advantages: Can raise capital from the public, credibility, limited liability.
- Disadvantages: Extensive compliance, complex management, costly to maintain.
Eligibility Criteria for Registering a Startup
To qualify as a startup in India, you must meet certain criteria under the Startup India Program:
- Must be registered as a Private Limited Company, LLP, or Partnership.
- Should be within 10 years of incorporation.
- Annual turnover must not exceed ₹100 crore in any financial year since incorporation.
- Should work towards innovation, development, or improvement of products or services.
Step-by-Step Process to Register a Startup in India
Here’s a detailed roadmap to legally register your startup:
Step 1: Choose the Type of Business Structure
- Evaluate your business needs, liability concerns, funding requirements, and future growth plans.
- Most startups choose Private Limited Company or LLP for ease of investment.
Step 2: Obtain Digital Signature Certificate (DSC)
- Required for online filings with MCA.
- Class 2 DSC is sufficient for directors.
- Can be obtained from government-approved vendors.
Step 3: Apply for Director Identification Number (DIN)
- Mandatory for all directors of a company.
- Apply online on the MCA portal.
Step 4: Name Approval
- Choose a unique name that reflects your business identity.
- Avoid generic or misleading terms.
- File RUN (Reserve Unique Name) application with MCA.
Step 5: Incorporation Filing
- Submit SPICe+ (Simplified Proforma for Incorporating Company Electronically) forms online.
- Attach necessary documents:
- Identity proof of directors (Aadhar, PAN)
- Address proof
- NOC from owner of registered office property
- Once approved, MCA issues Certificate of Incorporation.
Step 6: PAN and TAN Registration
- PAN (Permanent Account Number) is mandatory for taxation purposes.
- TAN (Tax Deduction and Collection Account Number) is required for TDS.
- SPICe+ process automatically integrates PAN and TAN applications.
Step 7: Opening a Current Bank Account
- Open a bank account in the company’s name.
- Required for financial transactions, investor funding, and tax payments.
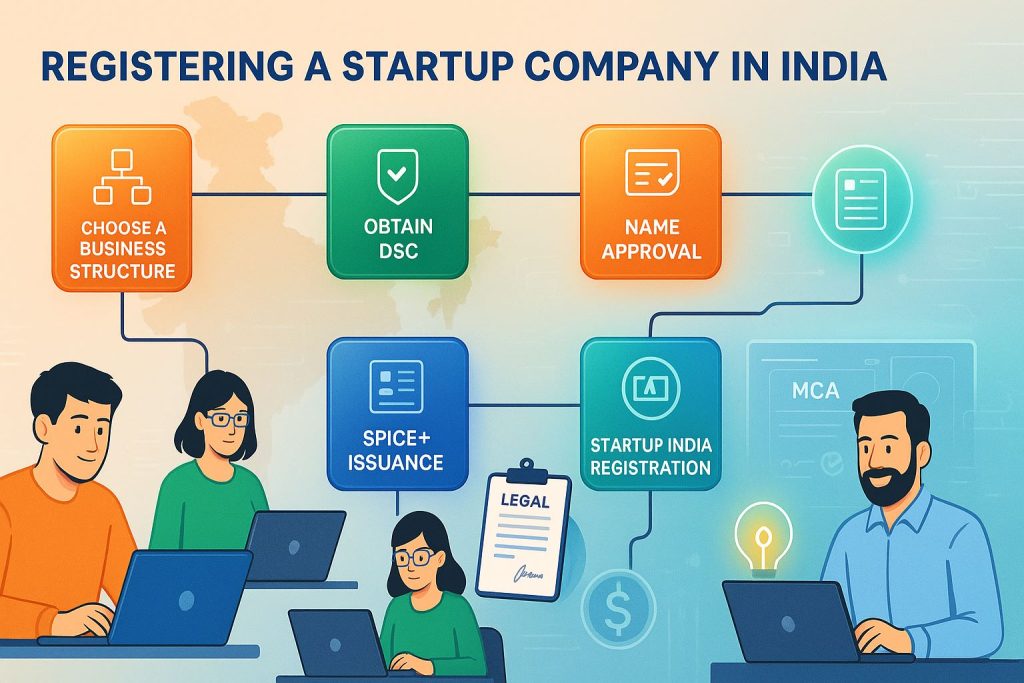
Registering Under the Startup India Program
The Startup India program provides additional benefits:
- Self-Certification: Exemptions from labor and environmental laws.
- Tax Benefits: 3-year tax holiday under Section 80-IAC.
- Funding Opportunities: Government-backed Fund of Funds and venture capital support.
- Easier Compliance: Fast-tracked patent application and regulatory approvals.
How to Register:
- Visit the Startup India portal.
- Create an account and submit:
- Company/LLP incorporation certificate
- PAN of the entity
- Brief description of innovation/product/service
Other Essential Registrations and Licenses
Depending on your startup type, you may require:
- Goods and Services Tax (GST) Registration: Mandatory if turnover exceeds ₹20 lakh.
- Professional Tax Registration: Required in some states.
- Shops and Establishment License: Mandatory for office operations.
- FSSAI License: For food-related businesses.
- Import Export Code (IEC): For export/import startups.
Taxation Benefits for Startups
Startups registered under Startup India enjoy:
- 100% Tax Exemption for 3 consecutive years.
- Exemption on Capital Gains: Long-term capital gains invested in startups are exempt.
- R&D Support: Government funding for research and innovation projects.
Common Challenges During Startup Registration
- Document Verification Delays: Incomplete or incorrect documents cause rejection.
- Name Approval Issues: Generic names or similarity with existing companies lead to delays.
- Compliance Complexity: Understanding labor laws, tax filings, and licenses.
- Lack of Awareness: Many entrepreneurs miss benefits like tax exemptions or funding schemes.
Tips for a Smooth Startup Registration Process
- Hire a Professional: CA or company secretary can simplify filings.
- Use MCA & Startup India Portals: Official portals minimize fraud and errors.
- Prepare Documents in Advance: Identity, address proofs, and office rent agreements.
- Check Name Availability: Ensure your brand name is unique.
- Plan Your Structure Wisely: LLP vs Pvt Ltd depending on funding and liability needs.
Conclusion
Registering a startup in India is now easier than ever, thanks to digital platforms and government initiatives.
Choosing the right business structure, complying with legal requirements, and registering under the Startup India program can open doors to funding, tax benefits, and credibility.
By following this step-by-step guide, entrepreneurs can not only ensure legal compliance but also position their startups for long-term growth and success.
Remember: Successful startup registration is a blend of careful planning, proper documentation, and leveraging government incentives effectively.
Start early, plan meticulously, and watch your entrepreneurial dreams turn into reality.


